Table of Contents
- Introduction to Type 2 Diabetes
- Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
- Causes and Risk Factors
- Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes
- Medication Options for Type 2 Diabetes
- Diet Chart for Type 2 Diabetes
- Lifestyle Changes and Exercise
- Preventing Complications
- Conclusion
Introduction to Type 2 Diabetes
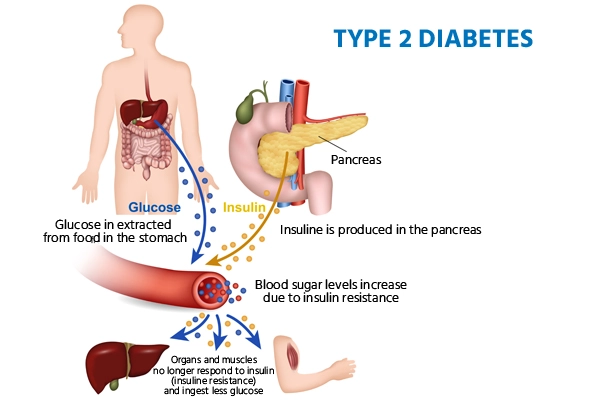
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose). Unlike type 1 diabetes, where the body doesn’t produce insulin, people with type 2 diabetes become resistant to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. This condition requires careful management of diet, exercise, and sometimes medication to maintain a healthy blood sugar level and prevent complications.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Recognizing the symptoms of type 2 diabetes early on can help in managing the condition effectively. Here are some common symptoms:
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores
- Frequent infections
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of type 2 diabetes is not entirely understood, certain factors increase the risk of developing it:
- Genetics: Family history of diabetes increases the risk.
- Obesity: Excess weight contributes to insulin resistance.
- Age: People over 45 are at higher risk.
- Physical inactivity: Lack of exercise is linked to insulin resistance.
- Poor diet: High intake of sugary or processed foods can increase risk.
By addressing these risk factors, you may reduce your chances of developing type 2 diabetes or manage its progression more effectively.
Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes
The primary treatment for type 2 diabetes focuses on managing blood sugar levels. This includes lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, regular exercise, and medication.
- Diet: Adopting a diabetes-friendly diet is essential. A balanced intake of whole grains, lean protein, healthy fats, and vegetables helps manage blood sugar.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, aiding blood sugar control.
- Medication: Depending on the individual, medication may be prescribed to help control blood sugar levels.
These treatments help in maintaining blood glucose within the target range and prevent complications associated with type 2 diabetes.
Medication Options for Type 2 Diabetes
Medication is often a critical component of treatment for type 2 diabetes. Here are some common medications:
- Metformin: Often the first medication prescribed, it lowers glucose production in the liver.
- Sulfonylureas: Medications like glipizide and glyburide increase insulin production.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors: These help remove excess glucose through the urine.
- DPP-4 Inhibitors: Drugs like sitagliptin work by increasing insulin production.
- GLP-1 Agonists: Injectable medications that slow digestion and reduce blood sugar levels.
Consult with your healthcare provider to determine which medication is most appropriate for you, based on your blood sugar levels and health needs.
Diet Chart for Type 2 Diabetes
Following a structured diet plan can significantly impact blood sugar management. Here’s a sample diet chart for people with type 2 diabetes.
| Meal | Food Options |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | Whole grain oatmeal with berries and a handful of nuts |
| Low-fat Greek yogurt with chia seeds | |
| Mid-Morning Snack | A small apple with almond butter |
| Lunch | Grilled chicken salad with leafy greens and olive oil |
| Lentil soup with mixed vegetables | |
| Afternoon Snack | Hummus with carrot sticks or cucumber slices |
| Dinner | Baked salmon with steamed broccoli and quinoa |
| Stir-fried tofu with mixed vegetables | |
| Evening Snack | A handful of walnuts or a sugar-free protein shake |
It’s essential to choose foods with a low glycemic index, which helps avoid spikes in blood sugar. Avoid sugary drinks, refined carbs, and processed snacks as much as possible.
Lifestyle Changes and Exercise
Exercise is a cornerstone of managing type 2 diabetes. It not only helps in controlling blood sugar but also reduces the risk of heart disease, which is often associated with diabetes. Try incorporating activities such as:
- Aerobic exercise: Brisk walking, jogging, or swimming can help control blood sugar.
- Strength training: Increases muscle mass, which can improve insulin sensitivity.
- Flexibility exercises: Yoga and stretching to enhance mobility and reduce stress.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week, along with strength training twice a week for optimal results.
Preventing Complications
Effective management of type 2 diabetes helps reduce the risk of complications, which can include:
- Heart disease: High blood sugar increases the risk of heart issues.
- Neuropathy: Uncontrolled diabetes can damage nerves, causing numbness or pain.
- Kidney disease: Elevated blood sugar can damage kidneys over time.
- Vision problems: Diabetes can lead to conditions like diabetic retinopathy, which affects eyesight.
Regular check-ups and monitoring of blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure are essential to prevent these complications.

Conclusion
Managing type 2 diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes, diet, exercise, and sometimes medication. By recognizing the symptoms early, adhering to a structured diet chart, and staying active, you can effectively manage blood sugar levels and improve your quality of life. Always work closely with your healthcare provider to tailor a treatment plan that suits your unique needs.
For more information on managing type 2 diabetes and dietary recommendations, visit American Diabetes Association.
Internal Link :https://neerajwaldon.com/arthritis-guide-types-symptoms-causes/