Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Health Cards
- Types of Health Cards
- Benefits of Health Cards in Emergency
- Immediate Cashless Treatment
- Access to Network Hospitals
- No Need for Immediate Cash
- Quick Access to Medical History
- How to Apply for a Health Card
- Conclusion: The Lifesaving Benefits of a Health Card
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)

Introduction to Health Cards
In today’s fast-paced world, emergencies can strike at any moment. Whether it’s an unexpected illness, accident, or any urgent medical condition, having quick access to healthcare is crucial. This is where a health card comes into play. A health card is more than just a piece of plastic—it’s a lifeline that can offer you peace of mind during medical emergencies. But what exactly is a health card, and how can it benefit you when you need it most?
Types of Health Cards
Health cards come in various forms, catering to different needs. Some of the most common types include:
- Insurance Health Card: Issued by health insurance companies, these cards offer cashless hospitalization at network hospitals.
- Government-Issued Health Card: Programs like Ayushman Bharat in India provide health cards that cover medical expenses for economically weaker sections.
- Corporate Health Card: Provided by employers to employees, these cards cover medical expenses under group health insurance policies.
Each type of health card offers unique benefits that can be a lifesaver in emergencies.

Benefits of Health Cards in Emergency
Let’s explore how a health card can make a significant difference during medical emergencies:
1. Immediate Cashless Treatment
One of the primary benefits of having a health card is access to cashless treatment. In case of an emergency, you can avail of medical services at a network hospital without worrying about upfront payments. The health card allows the hospital to directly bill your insurance provider, ensuring you receive timely treatment without financial stress.
- Example: Imagine being rushed to the hospital after an accident. With a health card, you can get immediate admission and treatment without the hassle of arranging cash or swiping a credit card.
2. Access to Network Hospitals
Health cards are usually linked to a wide network of hospitals, ensuring you have access to quality healthcare facilities. In an emergency, time is of the essence, and being able to reach a network hospital quickly can be crucial.
- Pro Tip: Always check the list of network hospitals associated with your health card to ensure you know where to go in case of an emergency.
3. No Need for Immediate Cash
During emergencies, arranging cash can be a daunting task, especially if you’re far from home or ATMs. Health cards eliminate this issue by providing cashless services, where the insurer settles the bill directly with the hospital.
- Did You Know? According to a recent survey, 65% of people face financial hurdles during medical emergencies. Having a health card can help mitigate this stress.
4. Quick Access to Medical History
Some health cards come integrated with your medical records, enabling healthcare providers to quickly access your medical history. This can be particularly useful in emergencies where prior health conditions or allergies need to be taken into account for accurate treatment.
- Real-Life Scenario: If you’re unconscious or unable to communicate, doctors can access critical information like blood type, allergies, and ongoing medications through your health card.
How to Apply for a Health Card
Applying for a health card is a straightforward process:
- Visit the Official Website of your insurance provider or government health scheme.
- Fill in the Application Form with necessary details like name, age, contact information, and medical history.
- Submit Required Documents, such as identity proof, address proof, and income certificates (for government schemes).
- Pay the Registration Fee (if applicable) and wait for your health card to be issued.
Many insurers and government programs also offer digital health cards, which can be stored on your smartphone for easy access.
that offer excellent benefits, especially during emergencies. These health cards are associated with leading health insurance providers and government schemes, ensuring comprehensive coverage and cashless services.
1. Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY)
- Eligibility: Available to economically weaker sections, especially rural families.
- Coverage: Up to ₹5 lakh per family per year for secondary and tertiary healthcare.
- Benefits:
- Covers hospitalization expenses, diagnostics, and follow-up care.
- No cap on family size or age, ensuring coverage for all eligible family members.
- Cashless and paperless treatment at over 25,000 empaneled hospitals across India.
Why It’s Great: Ideal for families below the poverty line, offering significant financial relief during emergencies without any premium costs.
2. Arogya Sanjeevani Health Card
- Provider: Offered by various insurance companies regulated by IRDAI.
- Coverage: ₹1 lakh to ₹5 lakh per year for hospitalization expenses.
- Benefits:
- Covers hospitalization, surgeries, ICU charges, and modern treatments like robotic surgeries.
- Includes pre- and post-hospitalization expenses for up to 30 and 60 days, respectively.
- Affordable premium rates, making it accessible for a wide range of people.
Why It’s Great: A standard health insurance policy designed to cover all essential healthcare needs with cashless hospitalization benefits.
3. Star Health Family Health Optima
- Provider: Star Health and Allied Insurance
- Coverage: ₹1 lakh to ₹25 lakh per family per year.
- Benefits:
- Cashless treatment at over 12,000 network hospitals.
- Includes coverage for day-care procedures, ambulance charges, and organ donor expenses.
- Offers a health card that simplifies the cashless claim process in emergencies.
Why It’s Great: Perfect for families looking for comprehensive coverage, including maternity benefits and emergency medical evacuation.
4. ICICI Lombard Complete Health Insurance Card
- Provider: ICICI Lombard General Insurance
- Coverage: ₹3 lakh to ₹50 lakh per year.
- Benefits:
- Cashless hospitalization at 6,500+ network hospitals.
- Covers pre- and post-hospitalization expenses, along with OPD treatments.
- Offers a wellness program that rewards policyholders for staying healthy.
Why It’s Great: Offers extensive coverage options, preventive healthcare benefits, and a robust network of hospitals for emergencies.
5. Max Bupa Health Recharge Card
- Provider: Max Bupa Health Insurance
- Coverage: Up to ₹25 lakh per year for individuals and families.
- Benefits:
- Cashless treatment at over 5,000 network hospitals.
- Covers both traditional and modern treatments, including robotic surgeries.
- Provides coverage for alternative treatments like Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy (AYUSH).
Why It’s Great: Ideal for those looking for extensive health coverage, including alternative treatments, with the benefit of cashless hospitalization.
6. HDFC ERGO Health Suraksha Card
- Provider: HDFC ERGO General Insurance
- Coverage: ₹3 lakh to ₹10 lakh per year.
- Benefits:
- Cashless hospitalization at over 10,000 network hospitals.
- Covers inpatient and day-care procedures, along with ambulance expenses.
- No sub-limits on room rent, ICU charges, or hospital fees.
Why It’s Great: Provides comprehensive coverage with no sub-limits, ensuring better financial protection during medical emergencies.
7. Religare Care Health Card
- Provider: Care Health Insurance (formerly Religare Health Insurance)
- Coverage: ₹3 lakh to ₹6 crore per year.
- Benefits:
- Cashless services at 8,300+ network hospitals across India.
- Includes coverage for pre-existing diseases after a waiting period.
- Provides coverage for critical illnesses, AYUSH treatments, and organ donor expenses.
Why It’s Great: Offers a wide range of sum insured options, making it suitable for both basic and high-end healthcare needs.
8. Aditya Birla Activ Health Platinum Card
- Provider: Aditya Birla Health Insurance
- Coverage: ₹2 lakh to ₹2 crore per year.
- Benefits:
- Cashless hospitalization at over 9,500 network hospitals.
- Rewards policyholders with “Health Returns” for staying fit and active.
- Includes coverage for chronic diseases like diabetes, asthma, and hypertension from day one.
Why It’s Great: Ideal for those who prioritize preventive healthcare and want rewards for maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Key Benefits of Health Cards in Emergencies
- Cashless Hospitalization: Most health cards offer cashless treatment, which means you don’t need to pay upfront during emergencies.
- Quick Access to Quality Healthcare: With a health card, you can get immediate medical attention at empaneled hospitals without financial stress.
- Reduced Out-of-Pocket Expenses: Health cards cover a significant portion of hospitalization costs, saving you from unexpected expenses.
- Wide Network of Hospitals: Access to a large network of hospitals ensures you get the best treatment wherever you are.
These health cards not only provide financial security during medical emergencies but also ensure timely access to quality healthcare services.
Conclusion: The Lifesaving Benefits of a Health Card
In times of medical emergencies, every second counts. A health card not only provides immediate access to healthcare services but also ensures that you receive quality treatment without the stress of financial burdens. Whether it’s cashless hospitalization, access to a network of hospitals, or quick retrieval of your medical history, the benefits of having a health card are undeniable.
Take Action Now: If you haven’t already, consider getting a health card to safeguard yourself and your family during unforeseen emergencies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is a health card?
A health card is a card issued by insurance companies, employers, or government health schemes, providing access to healthcare services, often with cashless benefits.
2. Can I use my health card at any hospital?
Health cards are usually accepted at network hospitals tied to your insurance provider or scheme. Always check the network hospital list before seeking treatment.
3. How long does it take to get a health card?
The issuance time can vary from a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on the provider. Some insurers offer instant digital health cards upon online registration.
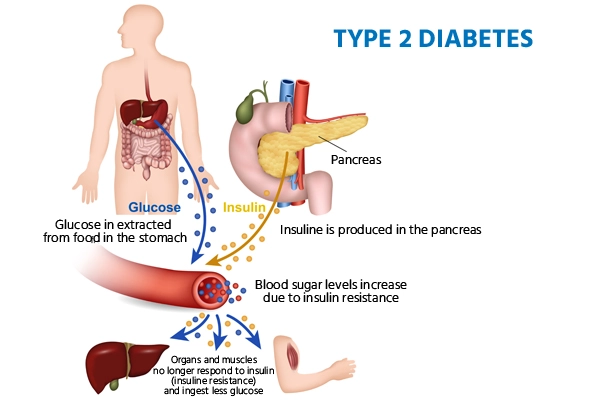
Internal Linkhttps://neerajwaldon.com/ultimate-guide-to-managing-type-2-diabetes/